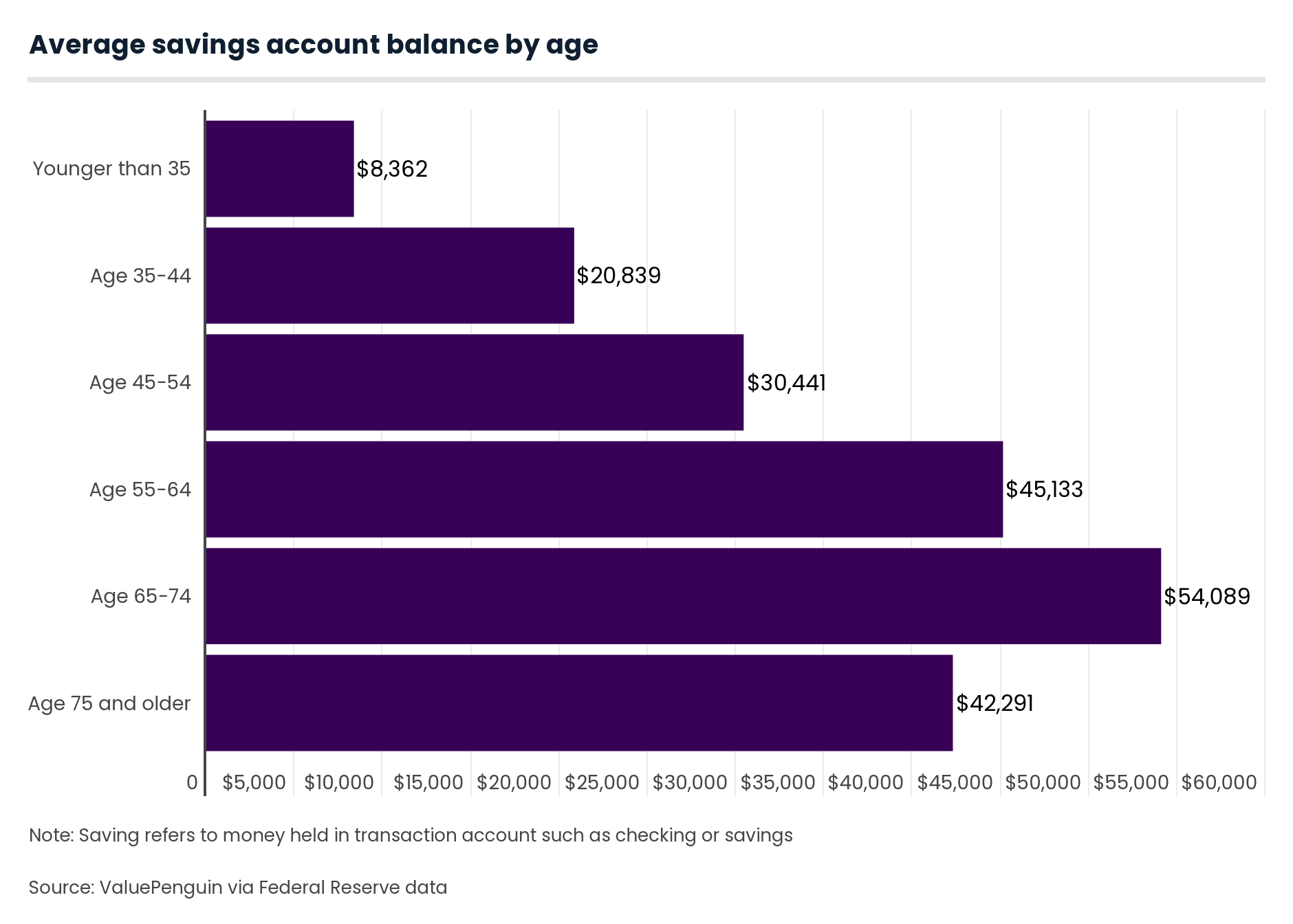
Understanding the concept of average savings by age is crucial for anyone looking to secure their financial future. It involves examining the typical amount individuals save at different stages of life, from their early twenties to retirement and beyond. Saving habits evolve as people progress through life, influenced by various factors such as income, expenses, and financial goals.
Average Savings by Age
Here, we will explore the importance of saving at different life stages and provide actionable strategies to help individuals achieve their financial objectives.
Building a Financial Foundation
In one’s early twenties, saving might seem like a distant priority, with many focusing on establishing their careers or pursuing higher education. However, this is precisely the time when laying the groundwork for financial stability becomes crucial.
By starting to save early, individuals can take advantage of compound interest, allowing their money to grow exponentially over time. Whether it’s setting aside a portion of each paycheck or investing in a retirement account, cultivating the habit of saving from a young age can yield significant long-term benefits.
Taking Advantage of Compound Interest
Compound interest is a powerful wealth-building tool that works best when time is on your side. By reinvesting the interest earned on savings or investments, individuals can generate additional earnings, leading to accelerated wealth accumulation.
In the context of average savings by age, harnessing the power of compound interest early on can make a substantial difference in one’s financial trajectory.
Even modest contributions made in the early years can grow into sizable assets over several decades, providing a financial cushion for the future.
Setting Financial Goals
Setting clear financial goals is essential for young adults embarking on their savings journey. Whether it’s saving for a down payment on a home, starting a family, or building an emergency fund, having specific objectives helps focus efforts and track progress.
By establishing SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) goals, individuals can create a roadmap for their financial future and stay motivated to save consistently.
Budgeting Effectively
Creating and sticking to a budget is a fundamental aspect of effective financial management. Young adults should track their income and expenses to identify areas where they can cut back and allocate more towards savings. Utilizing budgeting tools and apps can streamline this process.
Providing insights into spending patterns and helping individuals make informed decisions. By prioritizing saving and living within their means, young adults can lay a solid foundation for long-term financial success.
Balancing Financial Priorities
In one’s thirties, competing financial priorities often emerge, making it challenging to maintain consistent savings habits. From advancing in their careers to starting a family and managing debt, individuals may find themselves torn between various obligations.
However, prioritizing savings amidst these competing demands is crucial for building financial security. Automating contributions to retirement accounts and creating separate savings accounts for specific goals can help streamline the savings process and ensure progress towards long-term objectives.
Planning for Major Life Events
The thirties are a period of significant life transitions, from buying a home to starting a family and pursuing advanced education. Planning for these major life events requires careful financial foresight and preparation. Whether it’s saving for a down payment, funding a child’s education.
Or securing adequate insurance coverage, individuals in their thirties must anticipate future expenses and adjust their savings strategy accordingly. By proactively planning for these milestones, individuals can minimize financial stress and achieve their goals with confidence.
Assessing Retirement Savings
As individuals approach their forties, retirement planning takes center stage, with a heightened focus on long-term financial security. This involves assessing current retirement savings and determining whether they are on track to meet retirement goals. Utilizing retirement calculators and consulting with financial advisors can provide valuable insights into projected income needs and potential funding shortfalls.
By taking stock of their retirement savings in their forties, individuals can make informed decisions to bridge any gaps and ensure a comfortable retirement lifestyle.
Strategies to Boost Retirement Savings
For those lagging behind in their retirement savings, the forties present an opportunity to ramp up contributions and explore alternative savings vehicles. Catch-up contributions to retirement accounts, such as 401(k)s and IRAs, allow individuals aged 50 and older to contribute additional funds beyond the standard limits. Additionally.
Diversifying investments and considering higher-yield options, such as annuities or real estate, can help accelerate wealth accumulation in preparation for retirement.
Managing Expenses and Investments
In one’s fifties, individuals often find themselves balancing the competing demands of mid-life financial goals, such as saving for college tuition and funding retirement. Managing expenses becomes critical during this stage, as it allows individuals to free up resources for savings and investments.
Reviewing recurring expenses, negotiating bills, and downsizing where possible can help create additional financial flexibility. Simultaneously, optimizing investment portfolios to align with retirement timelines and risk tolerance is essential for maximizing long-term returns.
Reviewing Insurance Coverage
Mid-life is also a time for individuals to reassess their insurance needs and ensure adequate coverage for themselves and their loved ones. This includes health insurance, life insurance, disability insurance, and long-term care insurance.
As medical expenses tend to increase with age, having comprehensive health insurance coverage becomes increasingly important. Likewise, life insurance can provide financial protection for dependents in the event of unexpected death, while disability and long-term care insurance can safeguard against potential health-related expenses.
Evaluating Retirement Readiness
Approaching retirement in one’s fifties prompts a critical evaluation of retirement readiness. Individuals must assess whether they have accumulated sufficient savings to maintain their desired lifestyle throughout retirement.
This involves estimating retirement expenses, factoring in inflation, healthcare costs, and potential long-term care needs. Retirement calculators can help gauge whether current savings projections align with retirement goals and identify areas for adjustment or additional savings.
Catch-Up Contribution Options
For individuals in their fifties, catch-up contributions to retirement accounts present an opportunity to accelerate savings growth and bridge any retirement savings gaps. The IRS allows individuals aged 50 and older to make additional contributions to retirement accounts beyond the standard limits.
This includes catch-up contributions to employer-sponsored plans like 401(k)s and 403(b)s, as well as individual retirement accounts (IRAs). Leveraging these catch-up contribution options can significantly bolster retirement savings in the final years leading up to retirement.
Social Security and Medicare Considerations
Transitioning to retirement in one’s sixties involves navigating key decisions regarding Social Security and Medicare benefits. Understanding the eligibility criteria, claiming options, and potential impacts on retirement income is essential for optimizing benefits.
Delaying Social Security benefits beyond full retirement age can result in higher monthly payments, while enrolling in Medicare on time ensures access to essential healthcare coverage. Consulting with financial advisors and Medicare experts can help individuals make informed decisions tailored to their unique circumstances.
Adjusting Investment Allocations
As individuals enter retirement, their investment objectives often shift from accumulation to preservation of capital and income generation. Adjusting investment allocations to reflect this change in priorities is critical for mitigating risk and ensuring financial security throughout retirement.
This may involve reallocating assets towards more conservative investments, such as bonds and dividend-paying stocks, while reducing exposure to volatile equities. Additionally, implementing a systematic withdrawal strategy and periodic portfolio rebalancing can help sustain retirement income while managing investment risk.
Travel and Leisure Spending
Retirement offers individuals the freedom to pursue their passions and interests, whether it’s traveling the world, pursuing hobbies, or spending time with family and friends. Budgeting for leisure activities and travel expenses is an integral part of retirement planning, ensuring that retirees can enjoy their golden years to the fullest.
By allocating funds towards experiences and activities that bring joy and fulfillment, retirees can enhance their quality of life and create lasting memories in retirement.
Managing Healthcare Costs
As individuals age, healthcare costs often become a significant expense in retirement planning. From medical treatments to long-term care services, healthcare expenses can quickly deplete retirement savings if not adequately managed. Exploring healthcare options, such as Medicare supplemental plans and long-term care insurance.
Can provide additional financial protection against unforeseen medical costs. Additionally, maintaining a healthy lifestyle and staying proactive about preventive care can help minimize healthcare expenses in retirement.
Estate Planning and Legacy Considerations
In one’s seventies and beyond, estate planning becomes a crucial aspect of financial management, allowing individuals to outline their wishes for asset distribution and legacy preservation. This involves creating essential estate planning documents, such as wills, trusts, and powers of attorney, to ensure that assets are transferred.
smoothly and according to one’s wishes. Additionally, reviewing beneficiary designations and updating estate plans periodically can accommodate changing circumstances and family dynamics.
Long-Term Care Options
Long-term care considerations become increasingly important as individuals age and face potential health-related challenges. Term care insurance, annuities with long-term care riders, and self-funding strategies are among the options available to address long-term care needs in retirement.
Planning for long-term care in advance allows individuals to maintain control over their care preferences and protect their assets from the high costs associated with long-term care services.
Seeking guidance from elder law attorneys and financial advisors can help individuals navigate the complexities of long-term care planning and make informed decisions tailored to their specific circumstances. For more detail you may also visit Our Bioshint.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding average savings by age is paramount for securing financial well-being at every stage of life. By adopting proactive savings strategies, leveraging investment opportunities, and planning for future financial milestones, individuals can navigate the complexities of personal finance with confidence and achieve their long-term goals.
Remember, it’s never too early or too late to start saving for the future. Take control of your financial destiny today and pave the way for a secure and prosperous tomorrow.